This is one of the most common questions we get when we start an SEO project from scratch, and the answer is not at all simple as positioning depends on a large number of internal and external factors.
In this post, we are going to try to address this topic so you get a rough idea of how long positioning a web takes, depending on the type of keyword and the setting you are in.
SEO positioning is one of the most profitable services in digital marketing as once the top1 has been reached, all the traffic received through the search engine is highly profitable if we bear in mind that the effort of defending the position is less than that required to get there, and this is naturally much cheaper than paying to appear in a similar position in the sponsored results.
How long does positioning a web take?
The answer to this question is always it depends. No marketing agency can guarantee you an exact date when you will appear in the first page of Google.
There are a series of factors which influence how long positioning a web takes: it could be a week while on other occasions it might take up to a year. Or it might even never appear. We are going to explore some data, and at the end we will share some conclusions which may answer the question.
Some data on how long positioning a web takes
The SEO tool Ahrefs conducted a study of this. It highlights some interesting data which contextualise how many days or years it takes for a web to appear in the first page of Google. We include here some of the data we find most striking:
For instance, for two million keywords chosen at random, how long the top Google results have been there on average. We can see that the average age is over 600 days for each of the top 10 positions, or more than a year and a half on the first page, while for the top 3 results, this exceeds 800 days, or over two years.
Another revealing point is the percentage of pages which manage to occupy the first page of results in less than one year. In general, less than 5% of the more than 2 million pages analysed managed to position in less than one year, probably because these are searches where there is little competition or the webs are highly authoritative.
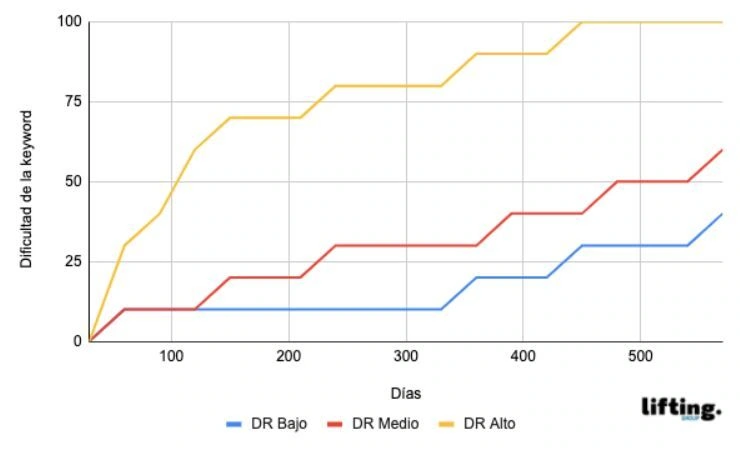
The graph below focusses on the search volume for keywords. As a general rule, the higher the number of searches, the stronger the competition. At Lifting Group, when we start to work on SEO positioning for a client, we centre on the main keywords (greater volume and competition) while we also work on longtail keywords, which are more specific searches with lower search volume, but easier to position because there will also be less competition. To do this, we optimise secondary pages or work on blog content.
In this way, longtail keywords start to appear on the first page of Google in 3-4 months, and our client will start to notice a rise both in web sessions and objectives met, while the main keywords slowly become positioned in parallel, as there are more competitors.
In short, everything will depend on the keyword it is desired to position and the authoritativeness of the domain employed. At one extreme, it will be very hard and time-consuming to position a difficult keyword with a recently registered domain. At the opposite extreme, it will be far easier to position a keyword with little competition employing a highly authoritative domain encompassing the topic in question.
Conclusion
As you have seen, there does not exist a precise answer to the question How long does positioning a web take?, as this will depend on the type of keyword we are to use and the competition. But we can give an estimate.
For keywords with little competition, in about 3-4 months you will start to notice a rise in positioning and web traffic. This will be seen progressively for more competitive keywords, until finally the business keywords where competition is stiff will also yield results.
Therefore, in an average of one and a half to two years, your main keywords will appear among the top Google search results. That being said, in some 3-4 months you will already be receiving more web traffic due to the positioning of longtail keywords.